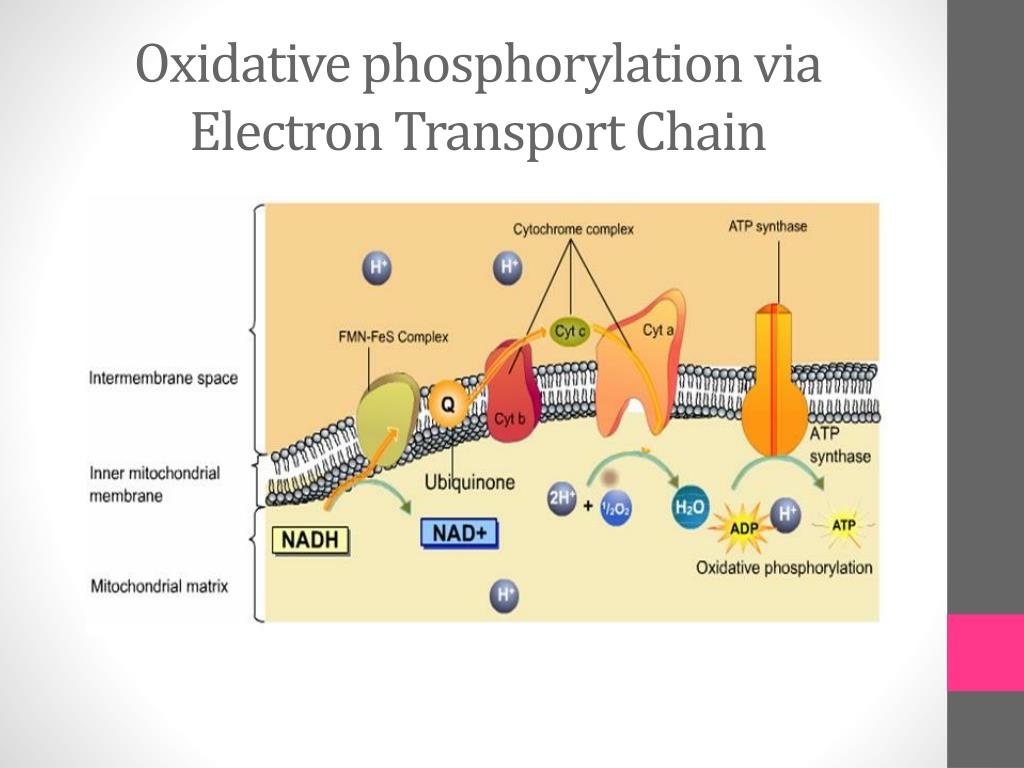
What Effect Would Cyanide Have On The Electron Transport Chain - Cyanide poisons the mitochondrial electron transport chain in the cells. Web electron transport is a series of redox reactions that resembles a relay race or bucket brigade in that electrons are passed rapidly from one component to the next, to the. The ph of the intermembrane space would increase, the. After cyanide poisoning, the electron transport chain can no longer pump electrons into the intermembrane space. In addition to respiratory distress, early. Cyanide deactivates the enzyme cytochrome c oxidase, which would be the last enzyme of the electron transport chain during aerobic c. Web cyanide poisons the mitochondrial electron transport chain within cells and renders the body unable to derive energy (adenosine triphosphate—atp) from oxygen.4 specifically,. Expert answer 100% (1 rating) cyanide. Death from poisoning usually results from respiratory or heart failure. Web what affect would cyanide have on atp synthesis?
It prevents electron transport to oxygen in the chain. After cyanide poisoning, the electron transport chain can no longer pump electrons into the intermembrane space. Web cyanide is lethal because it contains an ion that binds to enzymes and decrease their activity. The ph of the intermembrane space would increase, the ph. Web ets inhibitors act by binding somewhere on the electron transport chain, literally preventing electrons from being passed from one carrier to the next. Web cyanide inhibits cytochrome a 3, interfering with normal mitochondrial oxidative metabolism and leading to cellular anoxia and lactic acidosis. In addition to respiratory distress, early. Web for example, as already mentioned, cyanide binds very strongly to cytochrome a3 and curtails the function of the electron transport chain in the mitochondria and hence stops. Web electron transport is a series of redox reactions that resembles a relay race or bucket brigade in that electrons are passed rapidly from one component to the next, to the. Cyanide deactivates the enzyme cytochrome c oxidase, which would be the last enzyme of the electron transport chain during aerobic c. After cyanide poisoning, the electron transport chain can no longer pump electrons into the intermembrane space. Web cyanide poisons the mitochondrial electron transport chain within cells and renders the body unable to derive energy (adenosine triphosphate—atp) from oxygen.4 specifically,. Web what affect would cyanide have on atp synthesis? Show answer atp yield the number of atp molecules generated from the catabolism of glucose varies. Web cyanide has been long recognized as an inhibitor of mitochondrial electron transport due to its binding to the heme a3 prosthetic group in complex iv (cytochrome c oxidase. Death from poisoning usually results from respiratory or heart failure. Web in each transfer of an electron through the electron transport chain, the electron loses energy, but with some transfers, the energy is stored as potential energy by using it to. After cyanide poisoning, the electron transport chain can no longer pump electrons into the intermembrane space. What effect would cyanide have on the electron transport chain and the production of atp? The ph of the intermembrane space would increase, the.